How the solar storms that cause the Northern Lights can wreak havoc on Earth
How Solar Storms Can Wreak Havoc on Earth
Solar storms, also known as geomagnetic storms, are caused by disturbances in the sun’s magnetic field. These storms can have a range of…
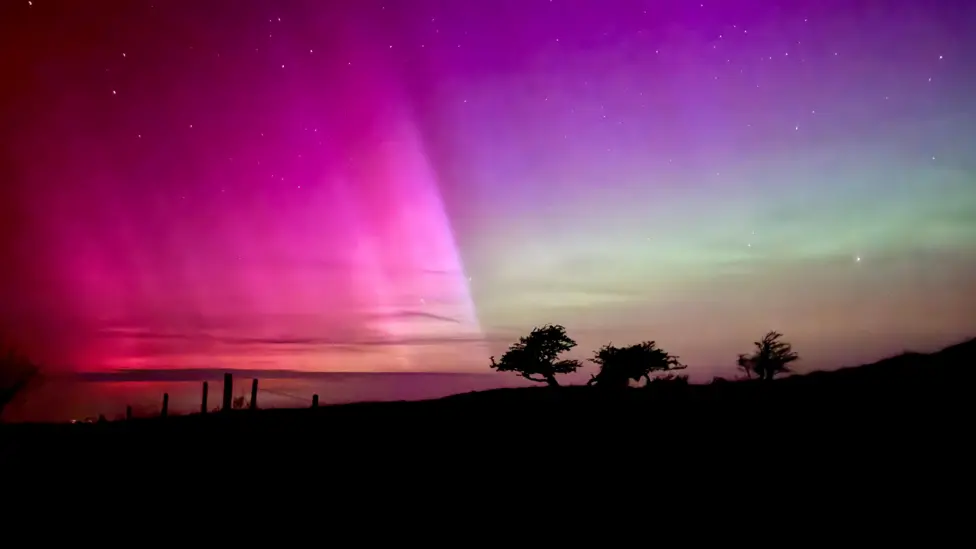

How Solar Storms Can Wreak Havoc on Earth
Solar storms, also known as geomagnetic storms, are caused by disturbances in the sun’s magnetic field. These storms can have a range of effects on Earth, including disrupting satellite communications, damaging power grids, and creating beautiful displays of the Northern Lights.
When a solar storm hits the Earth’s magnetic field, it can cause disruptions to GPS systems, radio communications, and other satellite-based technologies. This can lead to significant problems for industries that rely on these technologies for their day-to-day operations.
In addition to disrupting communication systems, solar storms can also wreak havoc on power grids. The intense electromagnetic radiation from a solar storm can induce currents in power lines, leading to widespread blackouts and damage to electrical infrastructure.
One of the most well-known effects of solar storms is the aurora borealis, or Northern Lights. These beautiful displays of light are caused by charged particles from the sun interacting with the Earth’s atmosphere. While the Northern Lights are a stunning sight to behold, they are also a reminder of the power of solar storms.
Scientists are studying solar storms to better understand their effects and develop strategies to protect critical infrastructure from their impacts. This research is crucial for ensuring the safety and stability of our modern technological society in the face of these powerful natural phenomena.
In conclusion, solar storms can have a range of disruptive effects on Earth, from disrupting communication systems to causing widespread power outages. While the Northern Lights may be a beautiful side effect of these storms, they are also a reminder of the potential havoc that solar storms can wreak on our planet.